For the past few years, autonomous vehicles have received an unprecedented welcome. Every automobile manufacturer is exploring ways to get in the business of autonomous vehicles as per their own capacity. While some people may consider the term “autonomous vehicles” to be the latest, but for technology enthusiasts, it is something that has been in the research phase for decades. In this lieu, the first practical approach was taken by the researchers of Stanford University by building a Stanford cart in 1961. This first autonomous cart like vehicle was capable of navigating through certain obstacles by way of the cameras and early developed AI algorithms. But it used to take about 10 to 15 minutes for the cart to move 1 meter.
Now you may be wondering about the time it takes to move 1 meter. But, in today’s reality, a lot of work is being done on the technological front. Therefore, it seems very absurd in today’s time to wait for such a long span to take a lap of just 1 meter. As compared to the past, the AI algorithms have improved a lot, design tools are in abundance, and research methods have been enriched with a lot of utilities. All these improvements pave the way for better autonomous vehicles. This is why, technological giants like Tesla, Uber, Google, Ford, and General Motors are in fierce competition to build effective and safe autonomous vehicles.
Building Blocks of an Autonomous Vehicle
There are a lot of technologies that serve the purpose of automation in different sectors. For example, programming brings automation in the software, while Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) brings automation in industrial machines. But since the automotive sector is a completely different regime and autonomous vehicles take into account different technologies. Therefore, it is better to say that the building of autonomous vehicles involves cross-collaboration of different building blocks having their own respective methodologies and working mechanisms. Following is the detail introduction to all those basic building blocks that are mandatory to build an autonomous vehicle:
Perception
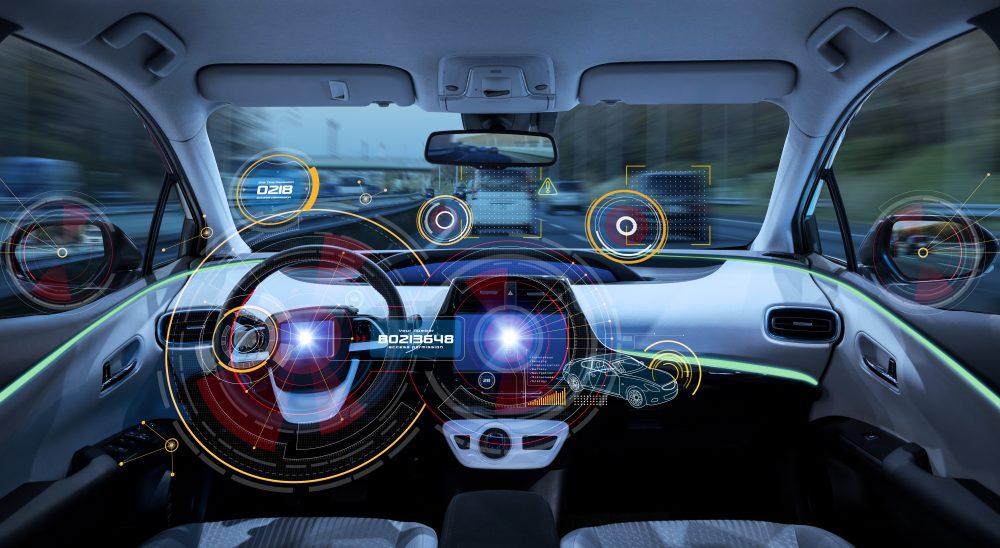
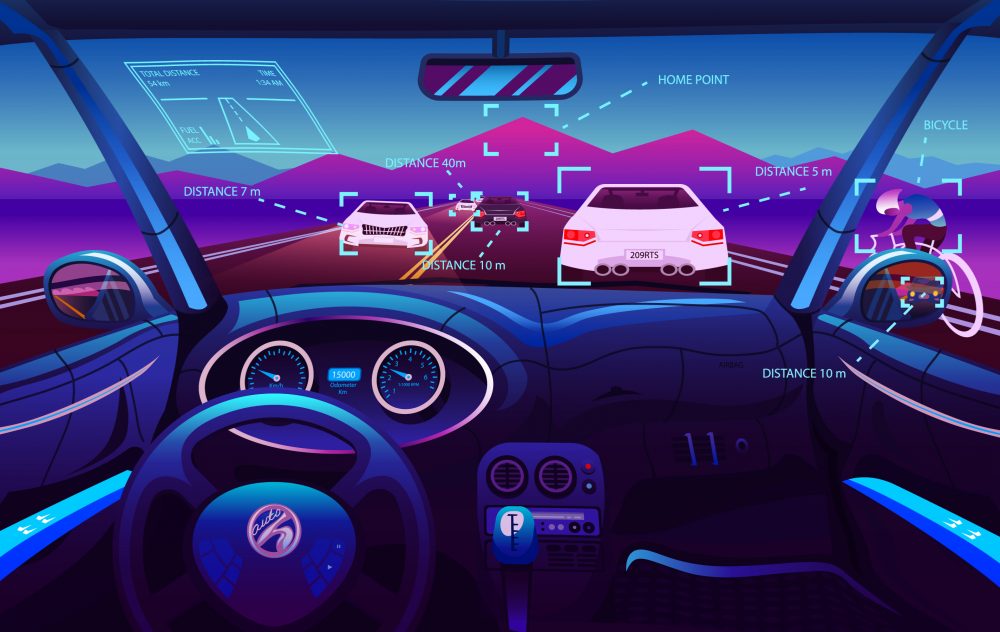
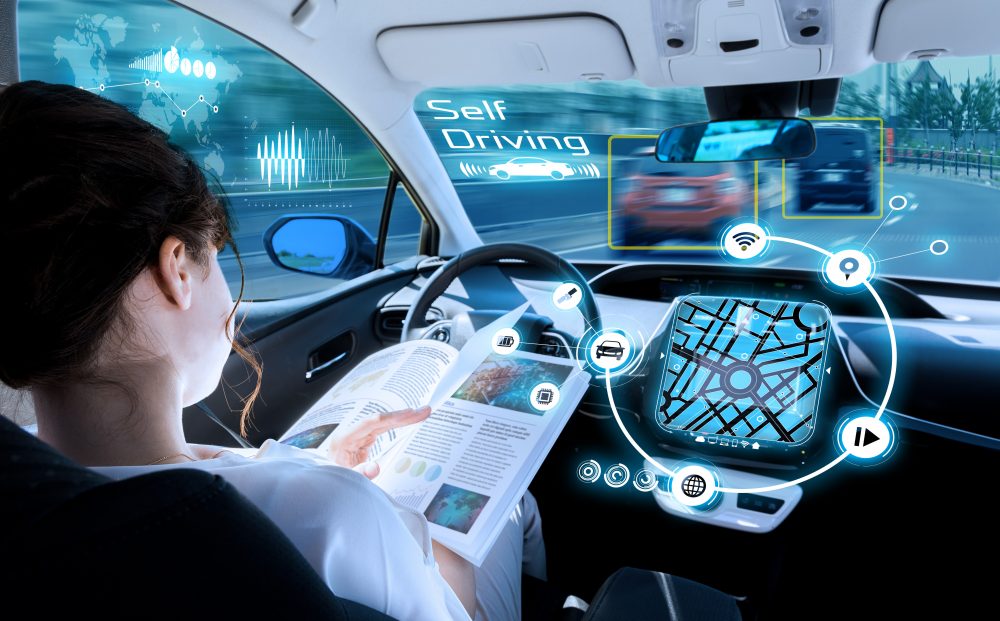
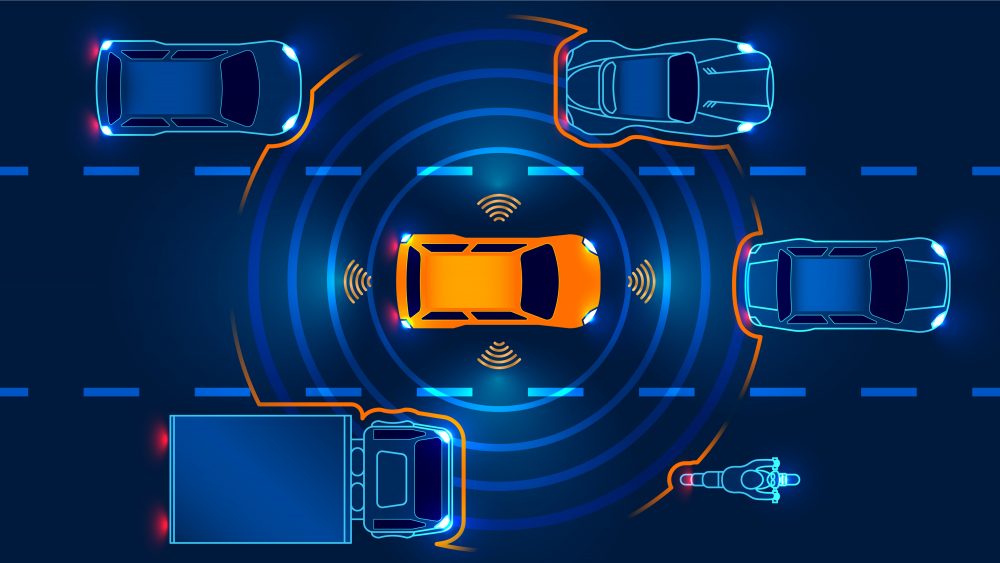
Perception in the world of autonomous vehicles is not the same as we perceive in the literal world. The concept of perception here uses the rich combination of high-tech cameras and sensors to get real-time data of the objects. As the first line of force, reliable and around the clock operations of perception is very crucial in the autonomous vehicles. The reason lies in its importance in the core decision making pertaining to different autonomous functions that an autonomous vehicle is supposed to perform. There are multiple perception elements, such as Radars, LiDARs, and a combination of certain cameras. Now one may question that since getting data is the main goal of perception and these requirements are very well being fulfilled by LiDARs and Radars, then why are cameras used? Basically, to get the in-depth information combinations of cameras, radars, and LiDARs, they are used in a process known as Sensor Fusion to not only label the objects but to confirm them too. For example, it is highly possible that radar may identify a body that is in front of the autonomous car and is moving with X velocity in the Y direction. But the camera will confirm whether this moving object is a car, cyclist, a pedestrian. This confirmation is very important from the perspective of autonomous vehicles, as the decisions are highly dependent on the type and nature of moving objects.
Interpretation
While perception is a sort of sensory component of the autonomous vehicle that senses the external parameters, interpretation is related to the translation of that sensing information into a sort of interpretive information. This is where algorithms like line following and obstacle detection are formulated. Interpretation is the software-based building block, and it is where intelligence will be embedded into the autonomous driving system. For example, when the perception stage has sensed an obstacle, then this gathered information is given to the interpreter. The interpreter will interpret this information and activates the given algorithm, which in this case, will be an obstacle avoidance algorithm.
Steering Model
This block or phase of an autonomous vehicle is a sort of an action phase. It is where practical demonstration of perception got from the sensors and the interpreted information comes into play. The steering model in the autonomous vehicle determines the angle at which the vehicle will steer left or right or maintain its position on the road. The basic driving force is the path following algorithm where steering is triggered at a specific angle to maintain position or move as per the defined settings. The steering is triggered with the help of a servo motor, which transmits the steering force via belt and pulley.
For example, imagine the sensing system senses the left turn sign on the road. It passes on this information to the interpretation that interprets the fed information in the form of the language the steering model understands. In accordance with the fed information, steering will be triggered at a certain angle to perform the left-turn action.
Control System
The control system is considered the heart of the autonomous vehicle. While the other three blocks build the platform, the control system makes sure that an autonomous vehicle gets driven on these platforms. Since constant feedback is being fed to the system to drive the vehicle up to the optimal conditions, a closed-loop control system is installed in the autonomous vehicles. Major components of the autonomous vehicle’s control system are acceleration, deceleration, and emergency braking systems. To ensure the safe and flawless driving of the autonomous vehicle, information such as deviation from the path, distance from the destination, obstacle, type of road, and any turning requirement are constantly being fed to the system, which then controls and operates the vehicle in an autonomous manner.
Conclusion
From the general perspective, autonomous vehicles may seem just an advanced version of today’s cars. But in reality, several complex processes not only make them better than today’s cars, but they also open a whole new paradigm of mobility. With the algorithms like path following, obstacle avoidance, and sheer adherence to road signs, road accidents can also be avoided. About 90 people die every day in the USA just because of road accidents. Human error is the main reason for road accidents. These 90 lives can be saved daily by adopting an intelligent and smart mobility mode, i.e., Autonomous Vehicles. With such a highly sophisticated and intelligent process of perception, interpretation, smart steering, and control system, we can stay assured that human errors can totally be negated. Because unlike humans, machines do not yawn and don’t get tired rigorously.